Data or information is a very crucial resource to us, therefore it's our responsibility to protect its confidentiality and integrity. While sending a message or information, unintended users might try to tamper with the message or might use its content for their good, or other unintended purposes, therefore we need some data hiding techniques to hide some confidential messages. The importance of data hiding techniques comes from the fact that there is no reliability over the medium through which the information is sent. In this blog, we will go through one of the data hiding techniques i.e., Image Steganography.
Steganography is a data hiding technique, which is used to hide information such as text, images, videos, etc. inside another image or video. Image Steganography is the technique of hiding text, images, audio inside an image.
So why do we need steganography when we have various encryption techniques to do the same? Let's take an example to understand that, suppose we want to encrypt a string "IEEE is an International Organization", the encrypted message may look something like "351@sbttr_$ee#^erh@_re8rry$#" or something similar to this based on the encrypting algorithm. The encrypted message often looks like something that makes no sense to the reader without decrypting it. This draws unnecessary attention and prevents us from hiding the presence of a string in it. Sometimes it's necessary to hide even the presence of encrypted information because no matter how strong an encrypting algorithm is, it can be cracked, or it might be necessary because of restrictions on encrypting a message in some countries. In such situations, steganography comes to our rescue. By using this data hiding technique, we can hide the presence of a message in it. We can see its example in the following two images, the first image is a host image, and the second image is the image obtained after encrypting the string "IEEE is an International Organization". The difference between the host and encrypted message is not visible to naked eyes.


Let’s take another example which shows the hiding of an image within an image


The first image is the host image which is used to hide the hiding image i.e., that is the second image in this scenario. The third image is the encrypted image which is the image obtained after hiding image2 in image1 using steganography techniques.
Steganography can be combined with encryption techniques to make a better algorithm.
Various Image Steganography Techniques:
There are a lot of image steganography techniques, which are based on LSB implementation, FFT, and CNN. Common FFT-based transformations are Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT), Quaternion Fourier Transformation (QFT), Discrete Fourier Transformation (DFT), Discrete Wavelet Transformation (DWT), and the Discrete Hadamard Transformation (DHT). In the LSB-based implementation, we make suitable changes in the LSB of each pixel value of the image to hide the data. In the FFT-based implementation, suitable changes are made in the magnitude of the host image's DFT to hide the information. This is because it is well known that for many images, the phase of the Fourier transform is more important than the magnitude. In this blog, we will discuss the implementation of image steganography using the LSB technique.
In computers, we represent every color as a combination of three fundamental colors i.e., red, green, blue. For instance, indigo color in computers is expressed as (75,0,130), where 75,0,130 represents the respective intensities of red, green, and blue channels.
We know that a digital image can be expressed as a multidimensional matrix. Consider a color image of width m and height n. Then the order of the matrix will be (n×m×3). The third dimension of the matrix represents the number of channels in the image. The following images will help visualize an image as a three-dimensional matrix.
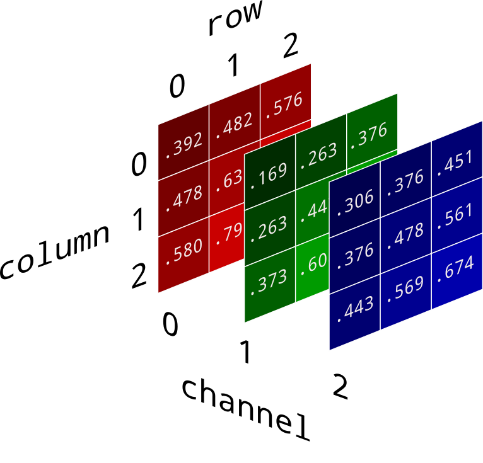
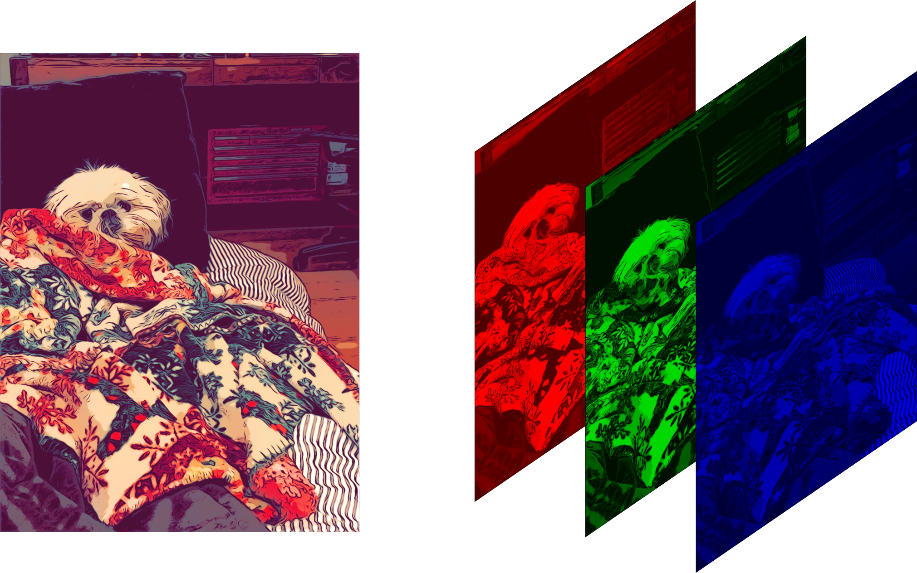
In a 24-bit RGB image, each channel pixel has 8 bits (1byte). So, the pixel intensities vary between 0-255 if we consider the data type to be uint8. The last bit of the bit is called LSB. The binary value of each channel's intensity for gray color is ( [01001011], [00000000], [10000010] ). If we change the LSB of each channel's intensity and make it ( [01001011], [00000000], [10000010] ), this little change in the color won't be visible to the naked eye. This idea forms the basis of image steganography. Suppose we want to hide a text message inside an image, then we first convert the message into binary and then take a single bit of the message, replace the LSB of the pixel value of the host image with the message bit. The following code is a simple way to do the same,
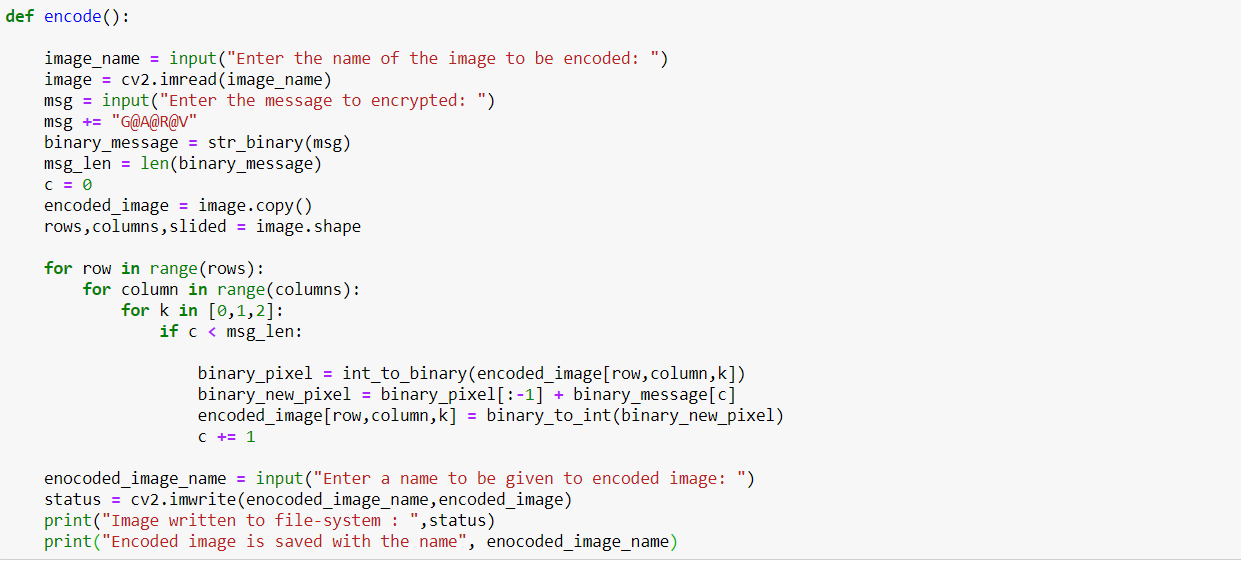
The code can be suitably modified to add an option of password for encoding as well as for decoding. For decoding the message from the encoded message, we take the LSB of the binary pixel intensities of the encoded image, stack them to make a binary message. This binary message is then converted into an 8-bit long byte, which represents a single decoded character. The following code is a simple way to do the same,
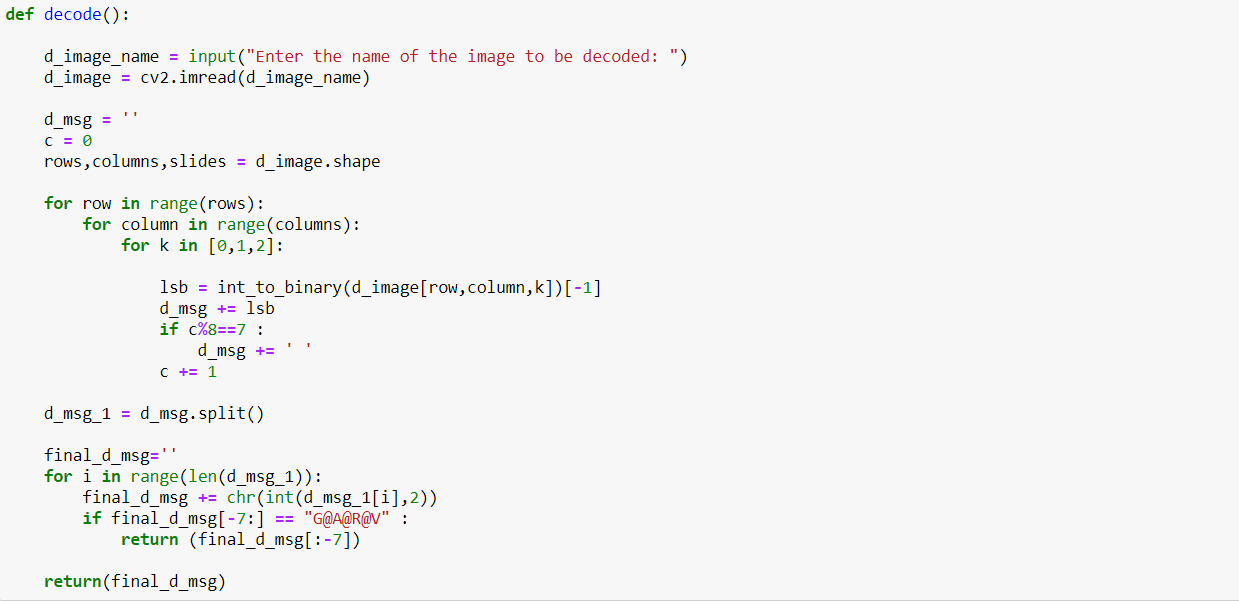
Similarly, we can write a code for hiding images within an image. One can consider, images as a 2-Dimensional array and text as a 1-dimensional array. This similarity can be used to expand the existing code to hide images.