The inherent need for human beings has always been to communicate and share information,albeit selectively. For this purpose, the information is to be coded in such a way that it can be deciphered only by the recipient, regardless of whether the recipient is right next to the sender or on the other side of the world. The communication channel is assumed to be plagued with adversaries..These adversaries have access to this coded information and are constantly trying to pry.So, the basic problem has always been to: transfer secure information over such insecure channels.
So, how DO you communicate when everyone is an adversary and nobody is trustworthy? The answer is simple.
"Cryptography is the art and science of making a crypto system that is capable of providing information security."
The primary objective of cryptography is to provide basic security services like data integrity, confidentiality, user-authenticity and non-repudiation.
Given below is a simple model of a crypto-system
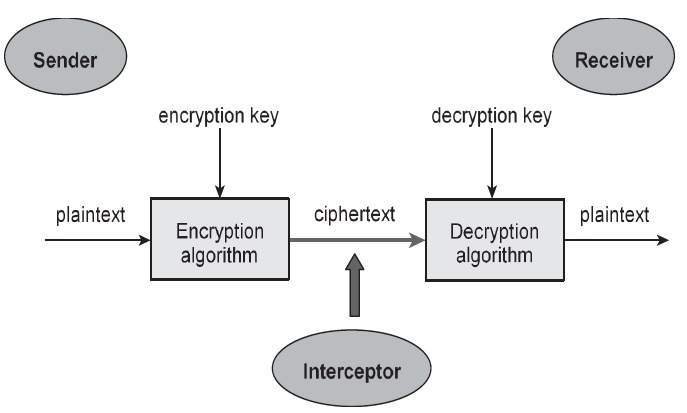
There are two types of crypto-systems,based on how the encryption is carried out.
Here, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption of the messages and such a key is established in advance by both the sender and the recipient.Thus,there has to exist "trust" between both sender and receiver, so as to not divulge the key.This was the most common method of encryption before the 1970's.
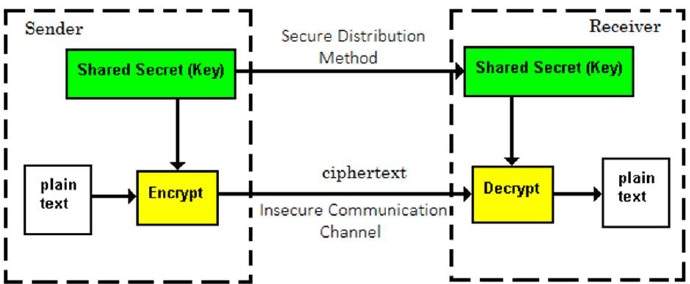
Suppose Alex wants to send a message to Carl using symmetric key encryption , then both of them will have to agree upon a key beforehand and use it to encrypt and decrypt the messages.
Here, two different keys are used for both encryption and decryption purposes and there exists some mathematical relation between the keys and thus decryption is possible.One of them is the private key and the other one is the public key.It is assumed that the private key is kept secret by a particular individual.
An individual(recipient) makes one of his keys public.A sender can encrypt a message with the help of this public key and such an encrypted message is transmitted over the insecure channel. Only the recipient can decrypt this message with the help of his private key, since he alone possesses it. This is clearly a more elegant solution than symmetric key encryption, that relies on "trust".
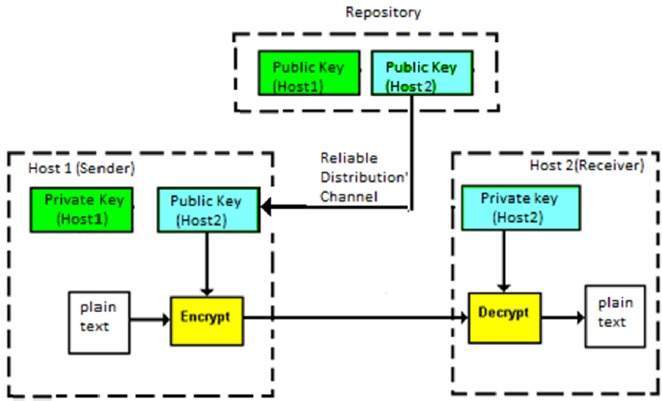
The crux of this system is to ensure that it is computationally infeasible to deduce the private key from the public key and the encrypted message.Obviously, it is important to ensure that the public key actually belongs to the recipient. This is usually accomplished with the help of a trusted third party, that hands out digital certificates.These parties are called Certificate Authorities(CA's).The public key is usually huge and is stored on such digital certificates whereas, the private key is stored on the system itself.
Also with public-key encryption systems, authenticity of digital systems or documents can also be ascertained with the help of Digital signatures. The content is signed with an individual's private key , and since the public key is easily available, the identity of the user is easily verified.
Suppose Alex sends a message(Using Carl's public key) and a digitally signed document to Carl, using a public-key encryption system, these are the advantages,in a nutshell:
1. It is possible to ascertain Alex's identity from his public key and digital signature on the document.
2. Only Alex could have signed the document,since he alone possesses the private key. Therefore it is not plausible for him to deny sending it.
3. Only Carl possesses the private key for decrypting the message. He,alone can decrypt the message.
4. When the signature is verified by Carl, it checks that the contents of the document or message match what was in there when the signature was applied. Thus, integrity of the data is preserved.
One of the major applications of public key cryptography is it's use in Secure Sockets Layer(SSL) protocol to ensure secure transactions between web browsers and servers.The protocol uses a CA to identify one or both end of the transactions.This,in short, is how it works:
1. A browser requests a secure page (usually https://).
2. The web server sends its public key with its certificate.
3. The browser checks that the certificate was issued by a trusted party (usually a trusted root CA), that the certificate is still valid and that the certificate is related to the site contacted.
4. The browser then uses the public key, to encrypt a random symmetric encryption key and sends it to the server with the encrypted URL required as well as other encrypted http data.
5. The web server decrypts the symmetric encryption key using its private key and uses the symmetric key to decrypt the URL and htp data.
6. The web server sends back the requested html document and http data encrypted with the symmetric key.
7. The browser decrypts the http data and html document using the symmetric key and displays the information.
Thus, as long as the CA is trustworthy, it is possible for the web browsers and servers to communicate securely and that is how all the information that is continuously exchanged on the internet stays safe and secure.