Imagine you are trying to train a dog to do fetch a ball. What you’d normally do is that you would reward it a snack every time it fetched the ball. The dog would then associate the snack with the act of fetching and would do it every time in the hope of a treat. Ladies and gentlemen, this is Reinforcement Learning. Cue the curtains. We’re done here. ;)
All jokes aside, Reinforcement Learning is the area of machine learning which resembles how we humans learn something. Attempt, Make mistakes, Learn, Master. The agents or the models learn for themselves to achieve successful strategies that lead to the greatest long-term rewards. This is a paradigm of learning from trial-and-error, solely from rewards or punishments.
Surely, you must have heard of DeepMind’s AlphaGo program? Yes, the one who beat the world No.1 ranked player in Go. This was built using RL.
Here we normally refer to the model as the agent. The agent is presented with an environment. This environment consists of states. In each state, an agent can take several actions. For each state-action pair, there is an associated reward which is collected when the agent takes this action in this state. For example, an agent playing a racing game would be rewarded every time it took the correct turn. This environment is represented by something known as the Markov Decision Process (MDP).
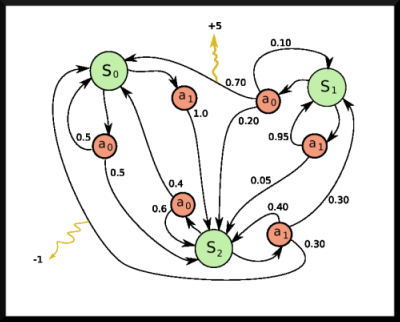
The job of the agent is to maximize the total reward as it interacts with the environment and moves through the states.
Reinforcement Learning is on the rise right now. I have already mentioned AlphaGo. A lot of current research focuses on using bots trained using RL to play video games. The same company DeepMind designed a Deep Q Network to play Atari games (paper link here). Also, OpenAI an AI research company founded by Elon Musk currently has a platform named Gym which is a toolkit for creating RL algorithms. Take a look if you’re interested.
In the industry, RL can be used to solve many problems requiring optimization. For example, when a modified e-commerce website has to be tested against its previous version to see which UI sells products better, A/B testing is used. Here, half of the users see the original website and the other half see the modified one. If the modified version of the site turns out to be doing better, this version is chosen. However, the website makes a small loss due to the fact that half of the users saw a suboptimal version of the site, hence losing a few purchases. This issue can be solved using Bandit Testing. This is based on the Multi Armed Bandit problem. Here, the division of users is only initially 50/50. A reinforcement learning model initially explores the two possibilities and after it figures out the better performing version, it exploits it. It starts reducing the percentage of the users who see the poorer performing version of the site so as to increase its reward, i.e. more purchases. By the end, the model will eliminate the poorer version completely.
First, you will need to define your environment. You should be able to define your problem as a MDP. You’ll need to define what the states are, what actions you can take in each state. Also, you’ll need to define a numerical reward for each state-action pair. Then if you’re using Q-Learning, you need to construct a Q-table consisting of Q values. These Q values corresponding to each state-action pair represents the discounted sum of rewards from the initial state to the current state. Using a table can cause data storage problems if there are many state and action pairs. We can instead use a neural network to estimate the Q value and determine the most optimal play. DeepMind used a Deep Q-Network to play Atari games. If you wanted to get started with Reinforcement Learning, Gym by OpenAI is a great place to start. Here are a few more resources to help understand the theory and get started with Reinforcement Learning: